So far, in the artificial intelligence industry, a major player was missing: Apple. Rumors had been circulating for some time that a proprietary GPT model was being developed in Cupertino’s labs, but until recently, no further information was available. Now, Apple has quietly released Ferret, an innovative, open-source, multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) capable of using image regions for queries. Ferret’s launch on Github occurred without major announcements or celebrations, with the code released alongside Ferret-Bench on October 30, followed by further updates on December 14. In this article, we will explore Ferret’s distinctive features, its comparison with Chat GPT-4, and implications for the future of AI at Apple.
“Non-Commercial Open Source”
Apple’s decision to make Ferret an open-source project under a non-commercial license means that it currently cannot be used for commercial projects. This release on Github is significant for researchers, as it shows Apple’s willingness to open up its AI work, deviating from its usual secrecy.
Differences Compared to Other LLMs
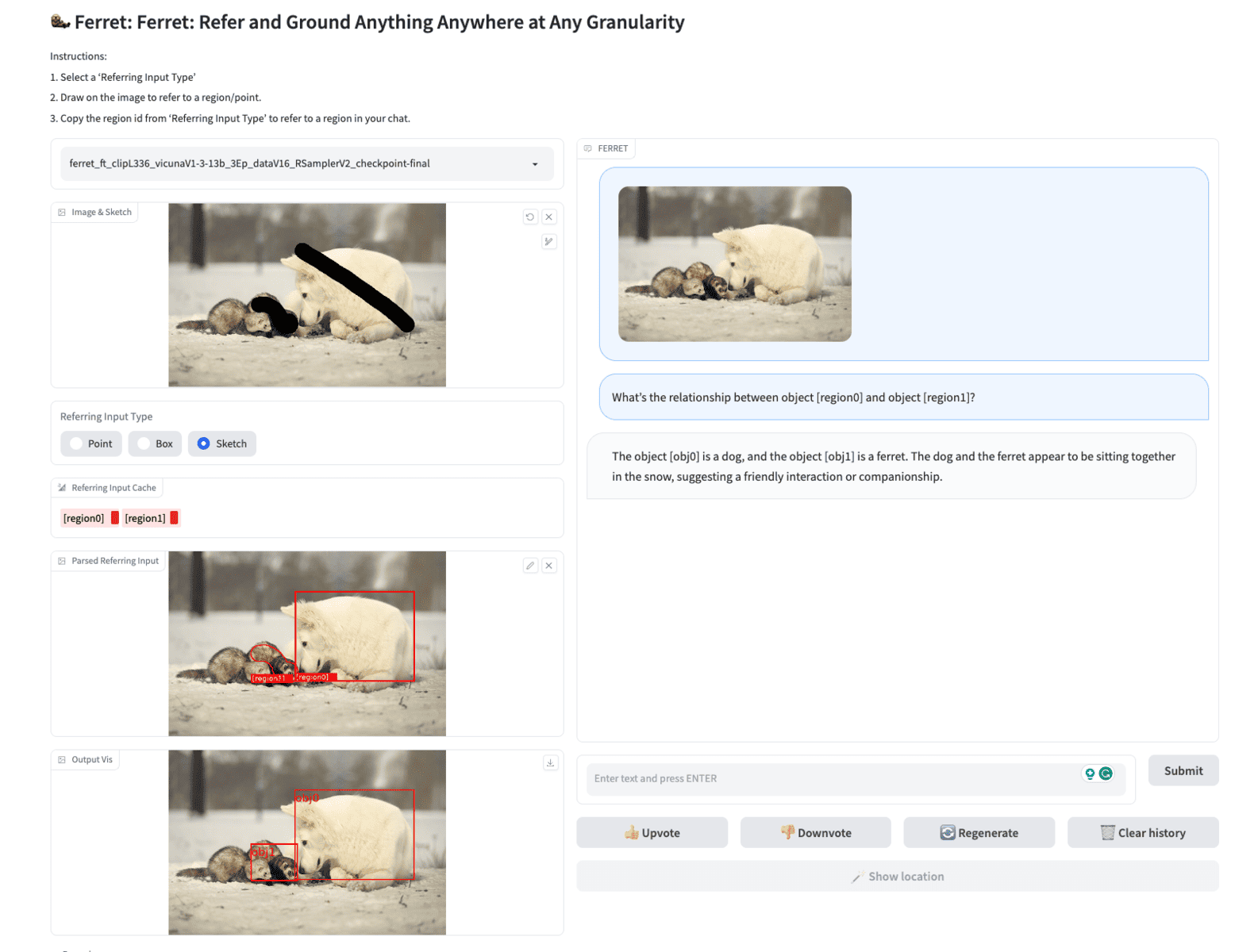
Unlike other models like GPT-4, Ferret specializes in precise referencing of objects in images. It can identify and describe specific areas and small details, surpassing GPT-4 in computational vision tasks. In comparative tests, Ferret outperformed GPT-4 in several benchmarks, especially in multimodal understanding and identifying objects in complex images.
Specialization vs. Generalization
While GPT-4 excels in general linguistic tasks, Ferret stands out for its ability to understand and analyze fine details in images, filling an important gap in current AI capabilities.
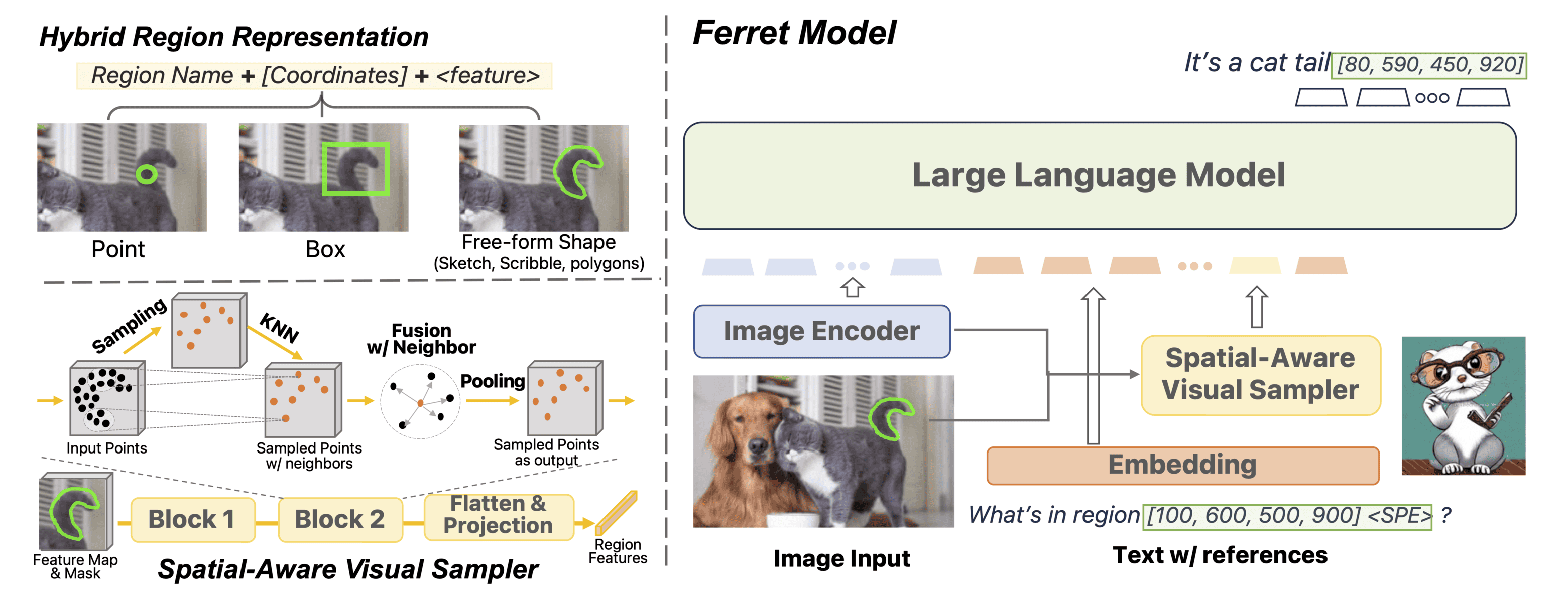
How Does Apple’s New Ferret Model Work?
The Ferret system utilizes multiple components to analyze both visual and textual inputs:
Visual Analysis with CLIP ViT: Uses the CLIP ViT model to analyze images and convert visual information into an AI-comprehensible format, identifying objects, shapes, and other details.
Language Understanding: Analyzes text prompts to convert them into a format processable by the system, understanding references to specific objects or regions in the accompanying image.
Understanding Reference Expressions: Combines visual and textual information, precisely localizing objects mentioned in text prompts within the image and providing detailed descriptions of the identified objects or regions.
Reference Accuracy
Ferret identifies and describes small and precise image regions more accurately based on textual prompts.
GPT-4, although good at understanding high-level scene comprehension, struggles with smaller details.
In the reference benchmarks outlined in Apple’s document, Ferret surpassed specialized models like GPT-4 ROI and Google’s Cosmos. It also performed very well against GPT-4 Vision in comparative tests on reference expressions.
Applications in Various Sectors
Ferret could significantly improve computer vision systems for autonomous vehicles, better recognizing objects in complex driving scenarios.
It is useful for detailed image annotations, VR/AR, visual chatbots, and more.
Expect a focus on excellence in AI visual understanding capabilities, particularly for the AR/VR sector and in enhancing Siri’s abilities.
Challenges and Strategies for Apple
Apple faces the challenge of expanding its AI infrastructure. While it is working to increase its AI server count, it may not currently have the capacity to compete on par with systems like ChatGPT. A potential solution could involve collaboration with other companies to expand capabilities, or continuing the strategy undertaken with Ferret, namely the release of an open-source model.
According to the New York Times, Apple is negotiating with news publishers to strike deals that would allow it to use their content to train its AI models, potentially competing with ChatGPT. Apple’s strategy involves an investment of at least 50 million dollars to secure deals with publishers, protecting itself from potential disputes. These deals would give Apple licenses to use articles and archives from these publishers, providing a rich dataset for training its generative AI models. High-profile publishers like Condé Nast and IAC, known for Vogue, The New Yorker, People, and The Daily Beast, are among those mentioned in discussions.
Conclusions
The introduction of Ferret marks a significant moment in the AI race among tech giants. Surpassing GPT-4 in key benchmarks, Apple asserts itself as a leader in specialized AI capabilities for detailed visual understanding. As Google, Microsoft, and others respond with their own computer vision transformations, Apple seems determined to compete in cutting-edge AI research and development. Ferret is not just a revolutionary AI model; it’s a symbol of Apple’s ambition and vision in the AI world, promising exciting innovations and significant advancements in artificial intelligence.
At Ex Machina, we are always searching for new solutions to use in our projects to create personalized solutions for companies and public entities. If you want to learn more about our AI solutions, visit our website > https://exmachina.ch